Parasites are pathogens that can inhabit the human body, animals and even some plants. There are many types of creatures in the world that penetrate the body of the host, feed on its nutrients, actively multiply and leave waste products in its body, which leads to the development of all kinds of diseases.
Worms are most common in humans. These are worms of various lengths and sizes that live mainly in the intestines of vertebrates. But some helminths can migrate throughout the body, invading muscles, liver, heart, joints, lungs and even the brain.
Worms damage the body of their host, so everyone should know how to determine the presence of parasites in the body. But many people do not want to go to the hospital, waste their time and be tested for helminths unreasonably.
In this case, one can find out if there are parasites in the body by paying attention to such an important criterion as the characteristic symptoms that develop in a particular type of helminthiasis. What if they don't exist? This is not happening!
However, in the early stages of helminth infestation, signs of vital activity of foreign microorganisms are weak or completely absent. The clinical picture becomes intense and expressed only with the active development of helminths, as their larvae can not parasitize in humans.
How to detect the presence of worms in the body without medical tests?
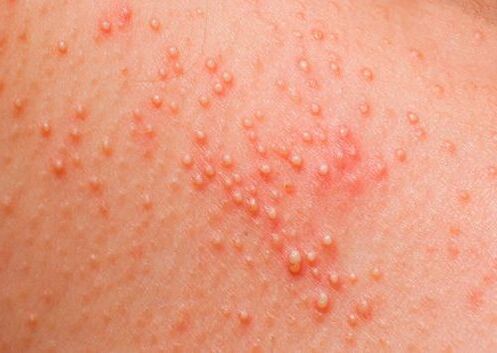
Different types of parasites cause characteristic symptoms in the host. If they are identified in time and correctly deciphered, then this will allow to determine the infection even at an early stage.
In this way the probability of misdiagnosis is minimized, which will allow proper and effective deworming with the help of folk or medical antiparasitic drugs.
So to identify parasites in the human body, you need to pay attention to the symptoms:
- Gritting teeth at night.
- Allergic skin rashes - acne, acne, urticaria, cold sores, eczema, red spots, papillomas, neurodermatitis, psoriasis and others.
- Development of diseases of the upper respiratory tract (bronchitis, pneumonia, runny nose), which is characteristic of ascariasis and strongyloidiasis.
- Abdominal bloating and diarrhea occur due to the fact that long worms interfere with the secretion of bile and pancreatic juice.
- Constipation occurs when worms form a ball that blocks the passage into the intestines.
- Discomfort in the joints and muscles due to the migration of parasites.
- Severe irritability provoked by painful symptoms.
- Persistent dry cough that cannot be treated with standard antitussive drugs.

There is also an increase in body temperature to subfebrile values. The causes of this condition can be hidden in allergies, blood intoxication, neurological disorders, disorders of the internal organs and brain, as well as anemic syndrome.
In addition, the worm that lives in a person significantly reduces his immunity, as a result of which the patient often suffers from colds. Also, the patient develops prolonged depression caused by intoxication of the body.
Typical symptoms of helminthiasis are nausea and vomiting, which are also caused by the release of toxic substances. In addition, some types of worms can live in the human body, producing specific hormones that affect the intestinal microflora, causing diarrhea.
However, in some cases, such symptoms are not attributed to helminthiasis, as they are similar to the signs of food poisoning. Although this can become a serious problem, because the later you start treatment, the more damage to the organs and systems of your host will have time to cause parasites.
Thus, in order to detect helminthiasis at home, a type of test must be performed. To this end, it is necessary to answer the following questions:
- Is there itching in the anus at night?
- Are the lymph nodes swollen?
- Are there skin rashes?
- How often does insomnia occur?
- Do you experience vomiting and nausea?
- Is there pain in the joints and muscles?
- How often does flatulence develop?
- How often does the taste of bitterness appear in the mouth?
If a person gives seven affirmative answers to these questions, then it can most likely be said that his body is infected with worms.
How to recognize the type of helminthiasis by symptoms?

At home you can determine which helminths inhabited the human body. But this can only happen if the parasitosis has reached the active phase of its development.
Ascariasis and diphyllobotriasis are characterized by neurological signs that are most intense in young patients. Aggressive behavior and increased nervousness are due to the effects of toxic substances on the nervous system. For similar reasons, an infected person develops migraines and dizziness.
As a rule, trichinosis is accompanied by pain in the joints and muscles, as well as swelling of the face and eyelids. This is due to the peculiarities of the life of Trichinella, which live in skeletal muscle. You can become infected with this parasite if you eat wild animal meat or pork that is poorly cooked.
Giardiasis affects the functioning of the liver and kidneys and provokes any allergic reactions. In addition, some people, when the body is damaged by giardia, suffer from arthritis, which develops as a result of intoxication. Also in an invasive patient the immunity is weakened, against this background the following diseases develop:
- sinusitis;
- stomatitis;
- bacterial vaginosis, etc.

A characteristic feature of pinworm enterobiosis is itching in the anal canal. In addition, most infected people experience gastrointestinal problems.
Anemic syndrome is characteristic of schistosomiasis. There are also manifestations of dysbiosis (pathogenic microorganisms inhibit the favorable microflora).
Cloronchiasis, fascionellosis and opisthorchiasis affect the gallbladder and develop icteric syndrome. In addition, against the background of the course of these helminthiases, the liver and spleen increase.
Strongyloidiasis manifests itself in various symptoms. So, with its progression, there are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, dyspepsia and allergic reactions.
How to determine if there are helminth eggs without laboratory conditions? When worms are in the breeding phase, it is quite easy to find out about their presence in the body. To do this, you need to take an analysis for the eggs of parasites.
With the development of opisthorchiasis, you can conduct your own research at home. For this purpose, tape or duct tape should be attached to the skin in the area of the anus.
It is best to perform this procedure immediately after waking up in the morning. If a person has opisthorchiasis, then his eggs will be identified on the adhesive surface of the tape.
Laboratory methods for the detection of parasites

If the patient has more than three characteristic symptoms of helminthiasis, then he should contact a medical institution to be able to confirm the laboratory determination of the presence of parasites at home.
The first step in case of suspected helminth infestation is stool examination. This allows you to identify tapeworm eggs, roundworms and flukes. However, to accurately confirm the diagnosis, tests should be done three times every few days.
To determine enterobiosis, scraping is performed near the anus. Also, one of the most accurate and convenient tests for the patient is ELISA, which allows you to detect antibodies in the blood that are produced by the body when parasitizing pathogenic microorganisms.
Sometimes a bioresonance diagnosis is performed to examine the frequency of the parasites. This method is very informative as it determines the condition of the body as a whole. In addition, in addition to parasites, such research allows you to understand the state of immunity that weakens it, to identify other diseases, as well as pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses.